Responsive Webdesign
Le Webdesign Responsive, c'est une affaire trés sérieuse
Le Webdesign ou la conception de votre site Web ainsi que le contenu integré, montrent votre vision de l’entreprise.
Un dicton bien connu dit : « La première impression est celle qui dure ». Dans les technologies web, votre site internet est la première entité qui interagit avec le visiteur, votre site web doit donc parler de lui-même !
Bien plus qu'une page Web
Avant d’utiliser un service de conception web en France, il est nécessaire de définir les objectifs de la marque, d’analyser la concurrence, d’identifier le public cible, de faire des recherches de mots-clés et d’élaborer une stratégie.
Design Réactif & Intuitif
Nous identifions votre charte graphique et établissons quelques ébauches de conception initiales pour un bon UX et choisissons un concept responsive.
Développement
Faire en sorte que le contenu, l’architecture de l’information, la conception visuelle fonctionnent ensemble pour atteindre vos objectifs.
Structure & Performance
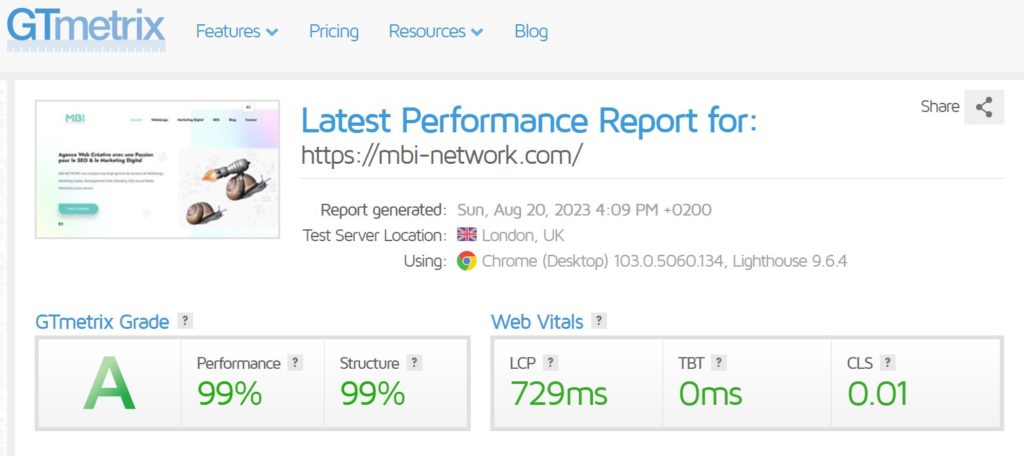
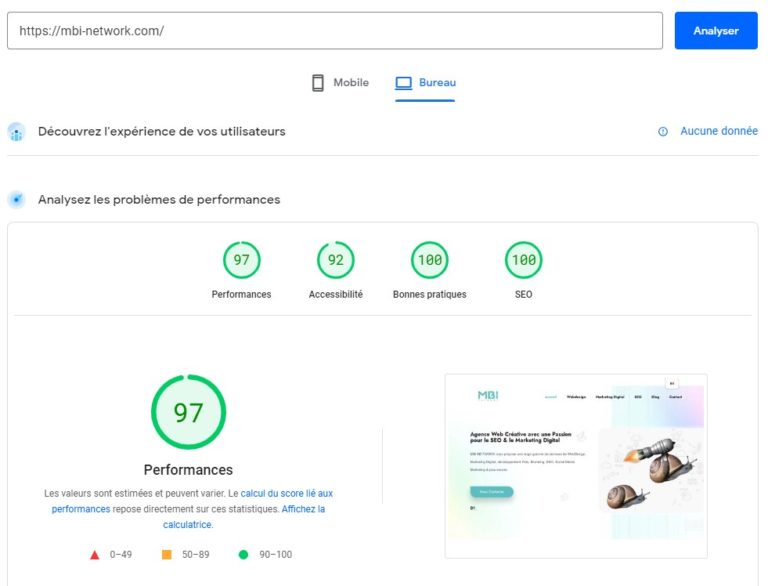
La structure et les performances d’un site web sont deux éléments essentiels pour le Webdesign et le SEO (Optimisation des Moteurs de recherche). Une structure bien conçue et organisée facilite la navigation pour les utilisateurs et aide les moteurs de recherche à comprendre le contenu du site. En d’autres termes, une structure claire et intuitive peut améliorer l’expérience utilisateur et le classement de votre site dans les résultats de recherche.
Les performances de votre site web, telles que la vitesse de chargement des pages et la réactivité, sont également cruciales pour le Webdesign et le SEO. Les utilisateurs s’attendent à des sites rapides et réactifs, et les moteurs de recherche prennent en compte les performances pour classer les sites dans les résultats de recherche. Un site lent ou peu réactif peut avoir un impact négatif sur l’expérience utilisateur et le classement de votre site dans les résultats de recherche.
En somme, la structure et les performances de votre site web ont un impact direct sur l’expérience utilisateur et le référencement de votre site. En gardant à l’esprit l’importance de ces éléments, vous pouvez créer un site web qui soit à la fois facile à utiliser pour les visiteurs et bien classé dans les résultats de recherche.
Les 3 Pilliers du Webdesign
La conception visuelle d’un site web englobe l’apparence générale du site, y compris le choix des couleurs, des polices, des images et de la mise en page. Le but est de créer un design esthétique, cohérent et professionnel qui reflète l’image de marque de l’entreprise et attire les visiteurs.
La conception visuelle
01.







02.
L'optimisation SEO
Cela implique de créer un site web qui est facilement accessible et indexé par les moteurs de recherche. Les éléments importants comprennent les balises de titre et les balises meta, la structure du site, le contenu pertinent et de qualité, ainsi que la vitesse de chargement du site. Le but est d’augmenter la visibilité du site web et d’attirer plus de trafic organique.I


03.
L'expérience utilisateur (UX)
Il s’agit de la façon dont les utilisateurs interagissent avec le site web et des émotions ressenties pendant leur visite. Un design efficace doit tenir compte des besoins des utilisateurs et les aider à atteindre leurs objectifs rapidement et facilement.
Il est également important de créer une expérience agréable, facile à comprendre et à utiliser pour les visiteurs.


E-Commerce Webdesign
Le e-commerce est devenu un élément incontournable de l’économie moderne, offrant une opportunité unique pour les entreprises de toucher un public mondial et de faciliter l’achat et la vente de produits et services.


Tout le monde sait que les magasins en détail sont une bonne affaire, peu importe ce que vous vendez. Aussi il y aura toujours des gens près de chez vous prêts à acheter vos produits ou services.
Mais un magasin est limité à sa situation géographique. Si vous voulez devenir International, optez pour le Webdesign d’un site E-Commerce; Il n’y a pas de limites à Internet.
Demandez Votre Devis Webdesign Gratuit
N’hésitez pas à nous contacter dès maintenant pour obtenir un devis gratuit et sans engagement. pour le Webdesign d’un site E-Commerce ou la conception web d’un site Vitrine à Paris, en France.
Nous sommes là pour répondre à toutes vos questions relatives à la conception de sites web en France et vous aider à trouver la solution qui conviendra le mieux à vos besoins.
Les Indispensables


Webdesign: Pertinence du Contenu
Dans le Webdesign, le contenu est la pierre angulaire d’un site internet réussi, car il attire les visiteurs, les engage et leur offre une expérience mémorable.
Un site web sans contenu pertinent et de qualité est comme une coquille vide, car il ne peut pas atteindre ses objectifs commerciaux ou communiquer efficacement avec les utilisateurs.
Contenu: Le Plagiat
Vérifier le plagiat dans le contenu d’un site internet est crucial pour maintenir l’intégrité et la crédibilité du site, et aussi éviter les éventuelles répercussions juridiques.
En vérifiant régulièrement le plagiat, les propriétaires de sites web peuvent s’assurer que leur contenu est original et de qualité, ce qui peut améliorer le référencement, renforcer la confiance des visiteurs et stimuler la croissance de l’entreprise.




Webdesign: Les Mots Clés
Lors de la conception de votre site, les mots clés sont essentiels pour le référencement d’un site internet, car ils permettent aux moteurs de recherche de comprendre le contenu et de le classer en fonction de sa pertinence pour les requêtes des utilisateurs.
En utilisant des mots clés pertinents et bien choisis dans leur contenu, vous pouvez attirer un trafic organique qualifié vu que vous aurez un bon UX ( Expérience Utilisateur), améliorer votre visibilité en ligne et augmenter les chances de conversions et de ventes.



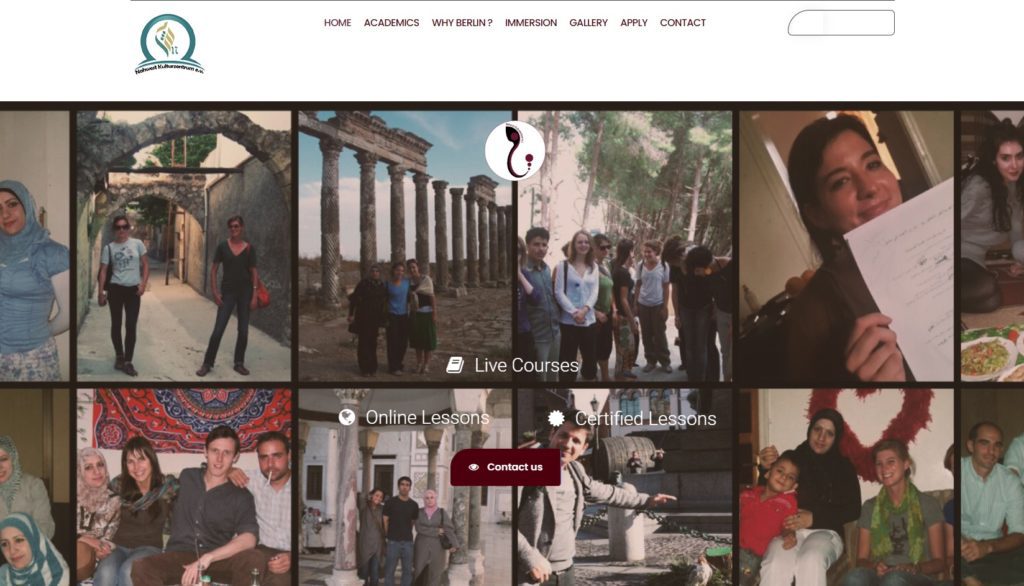
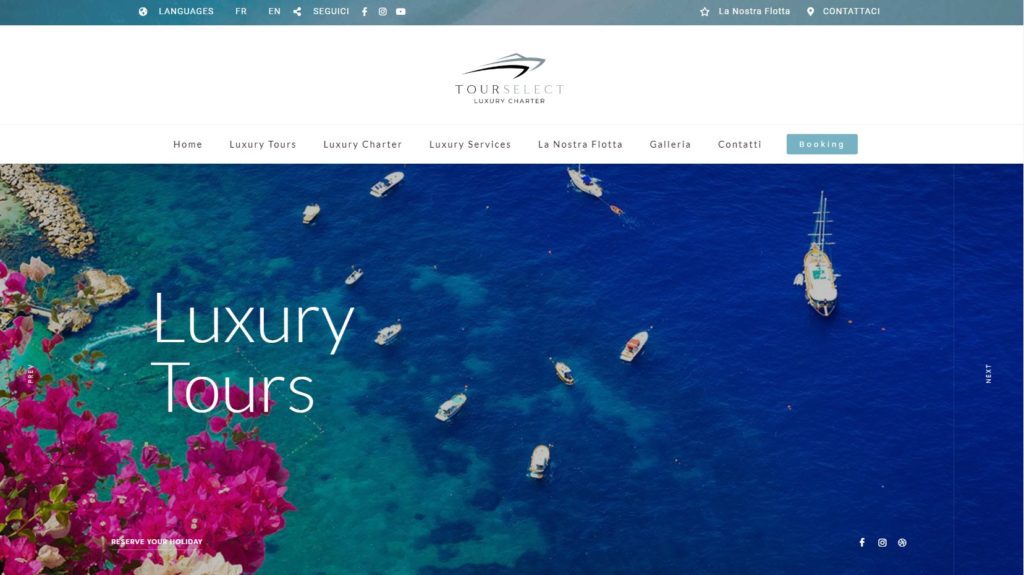
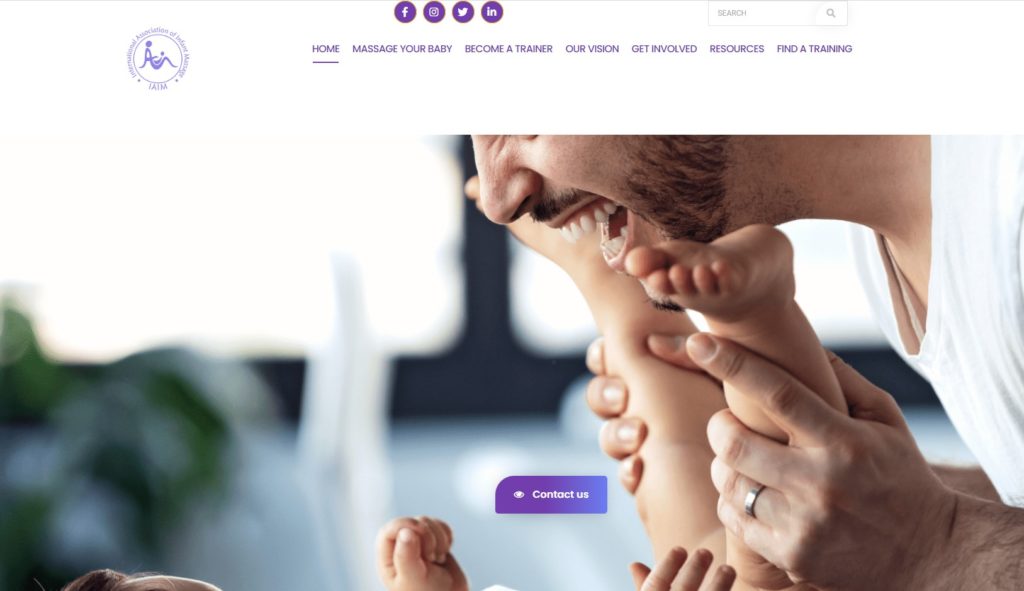
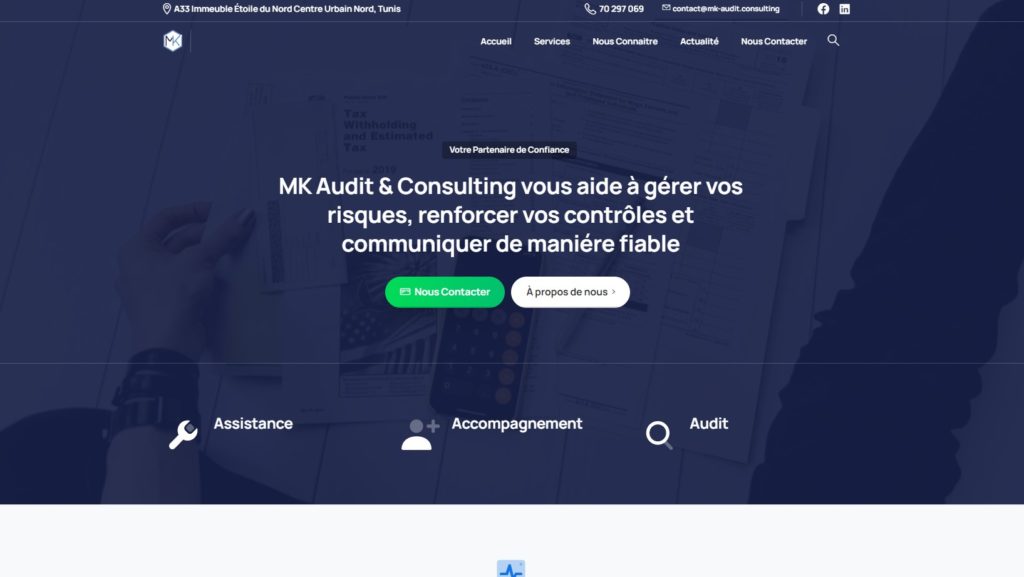
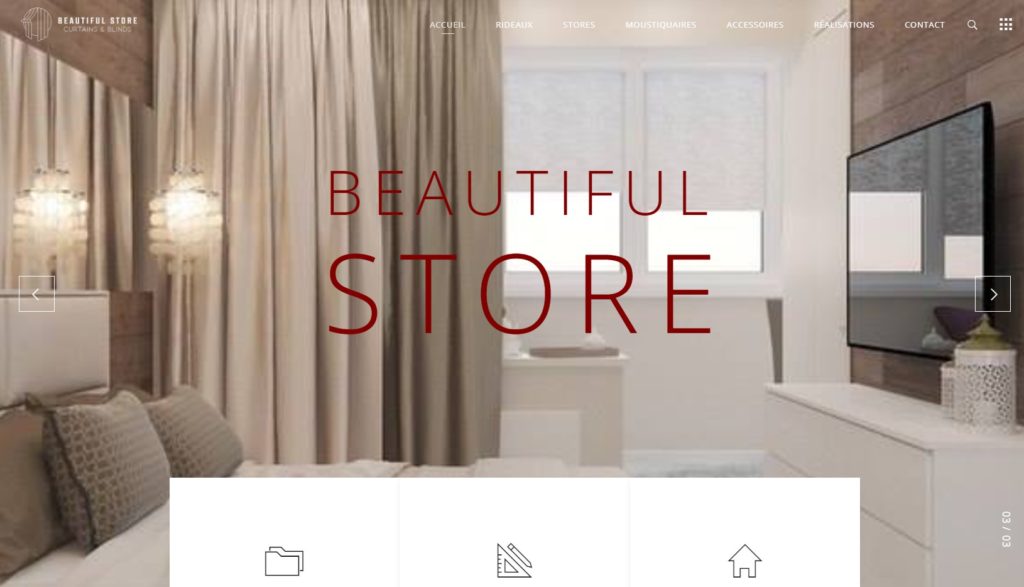
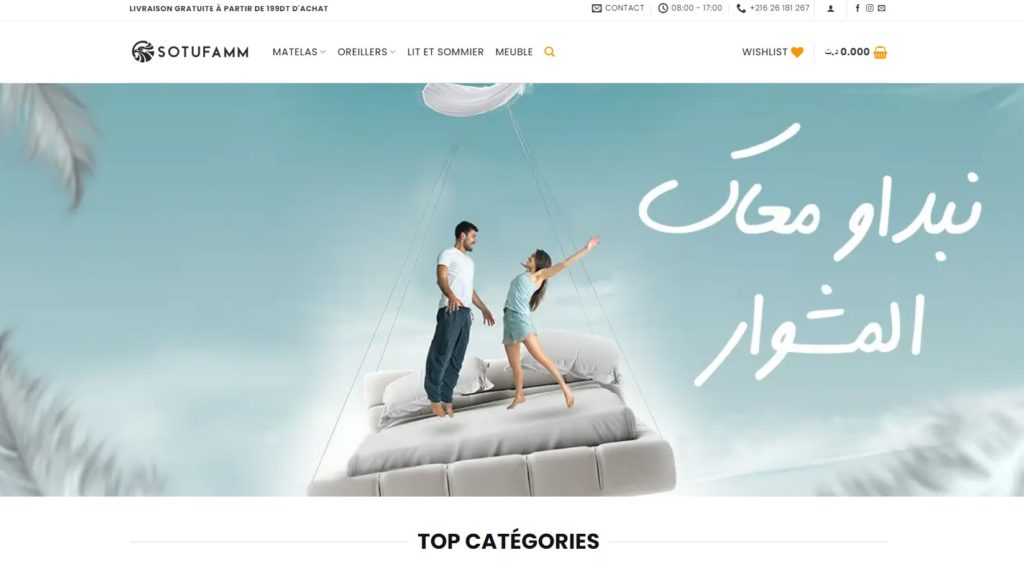
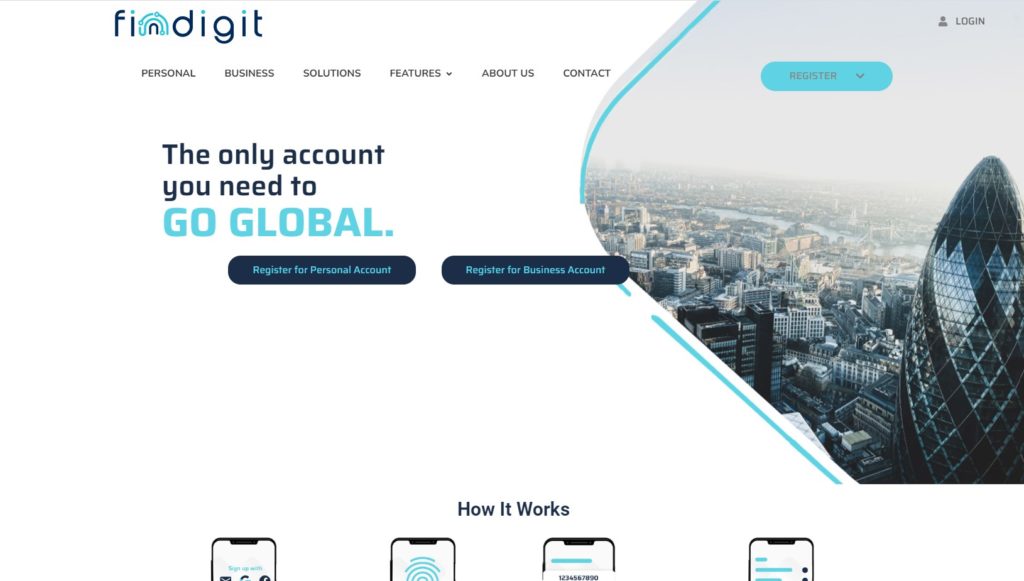
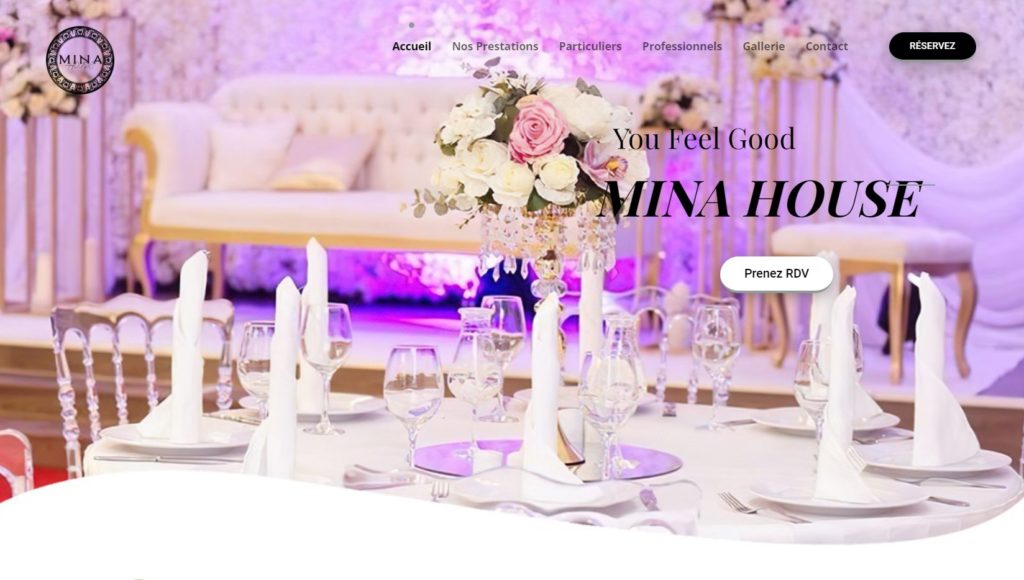
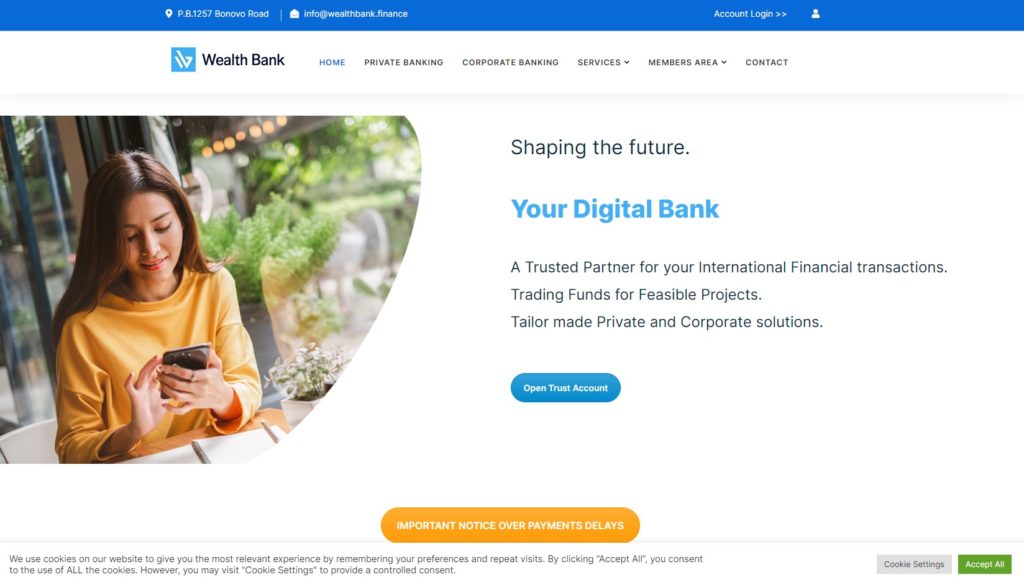
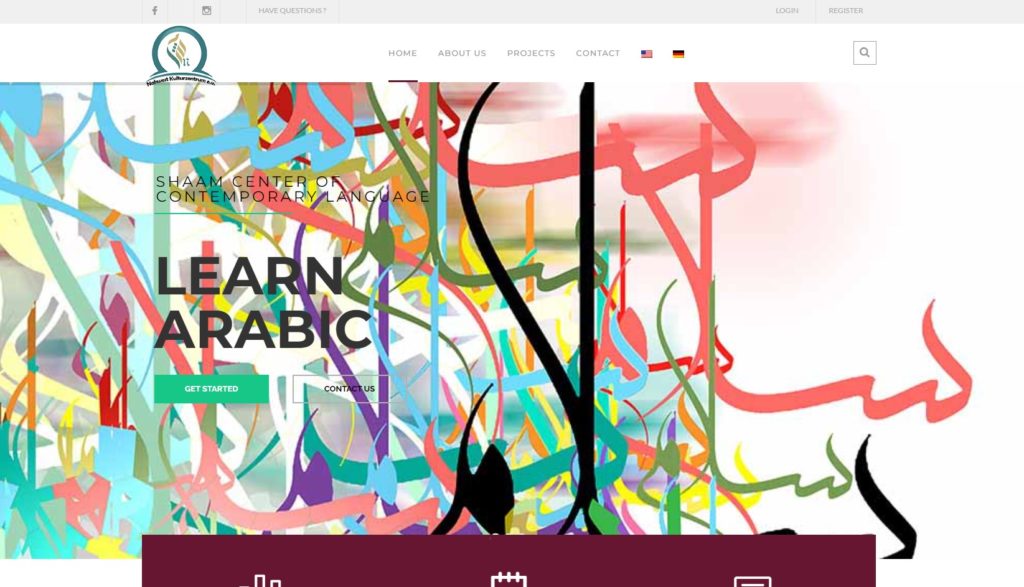
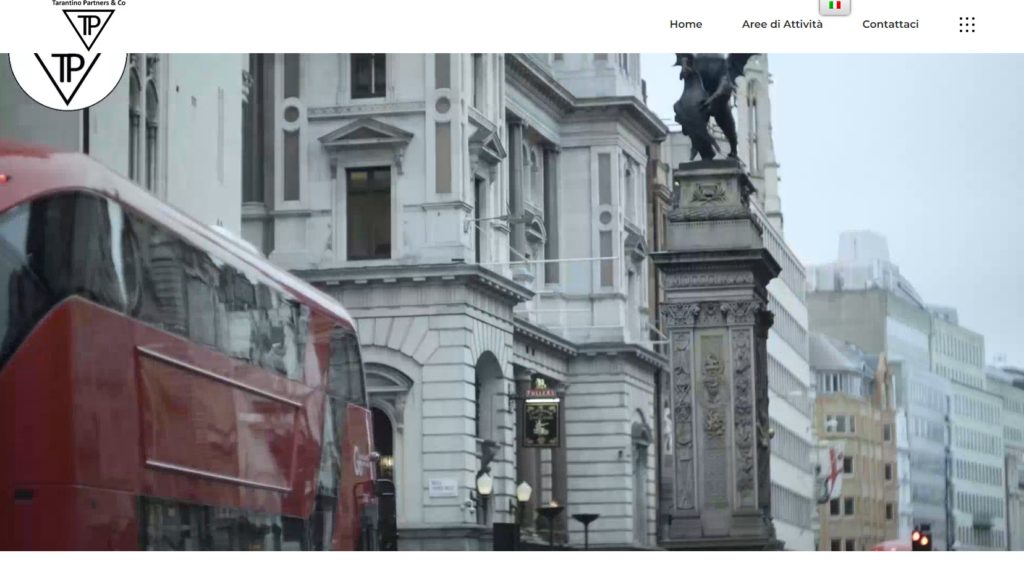
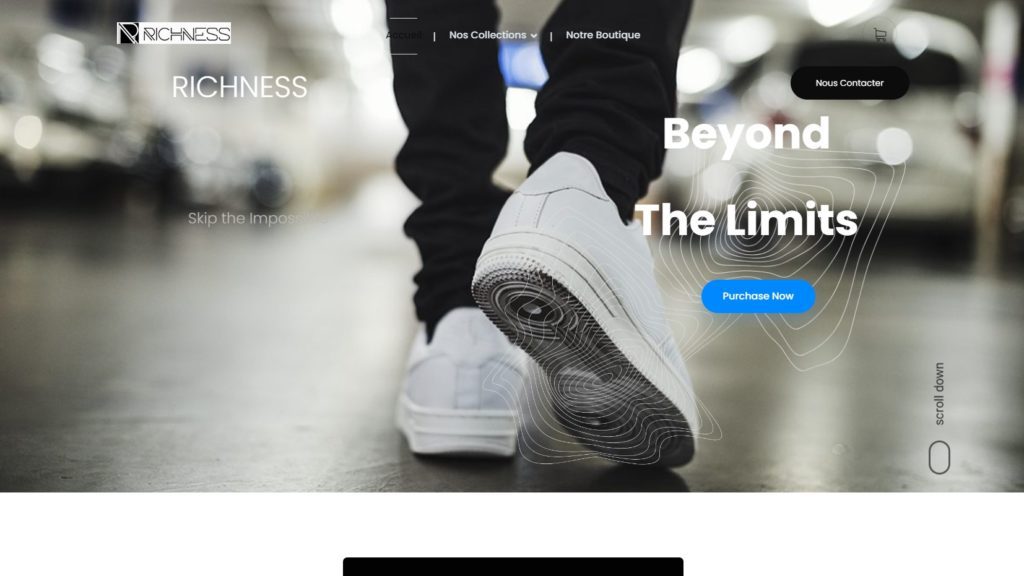
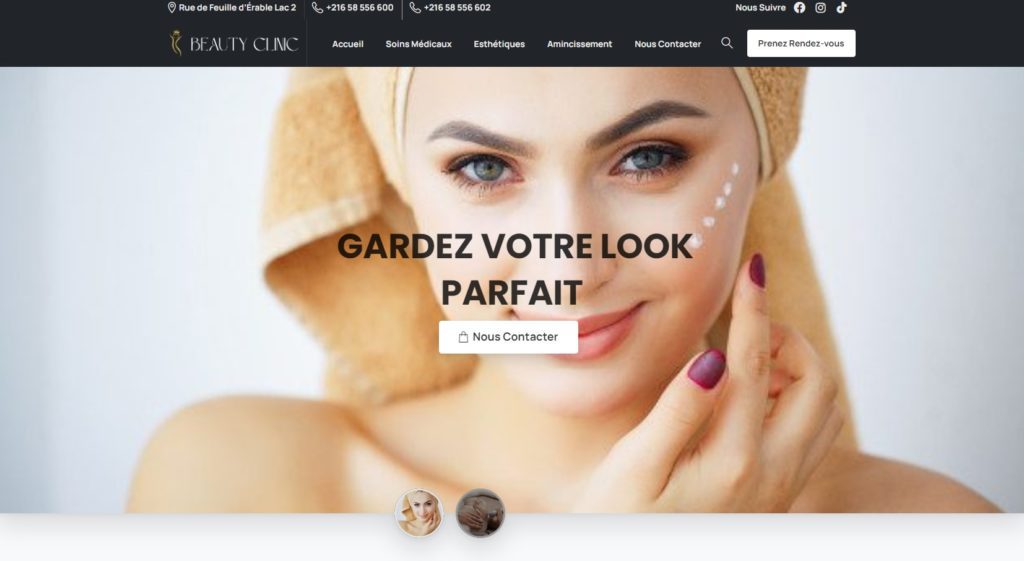
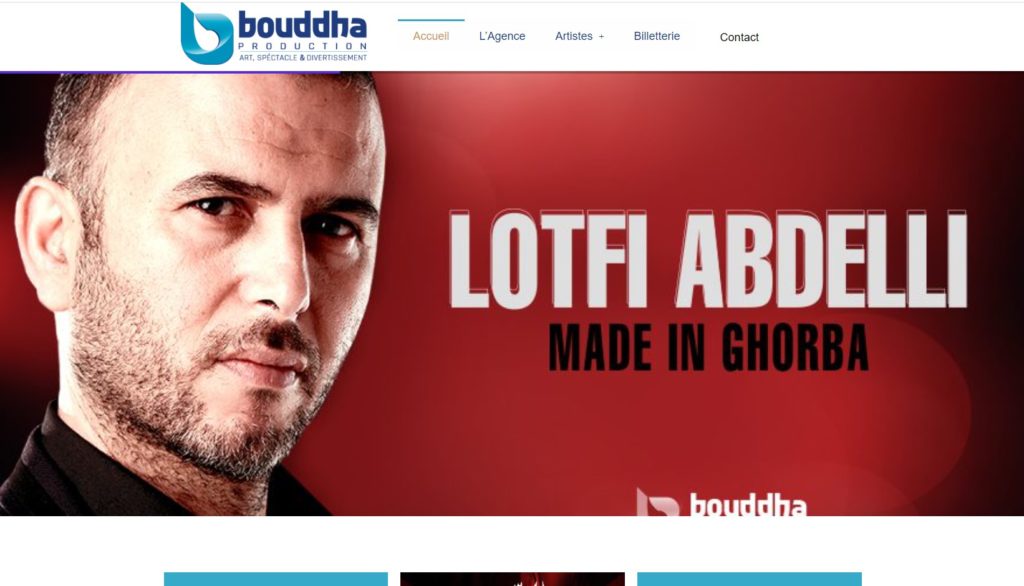
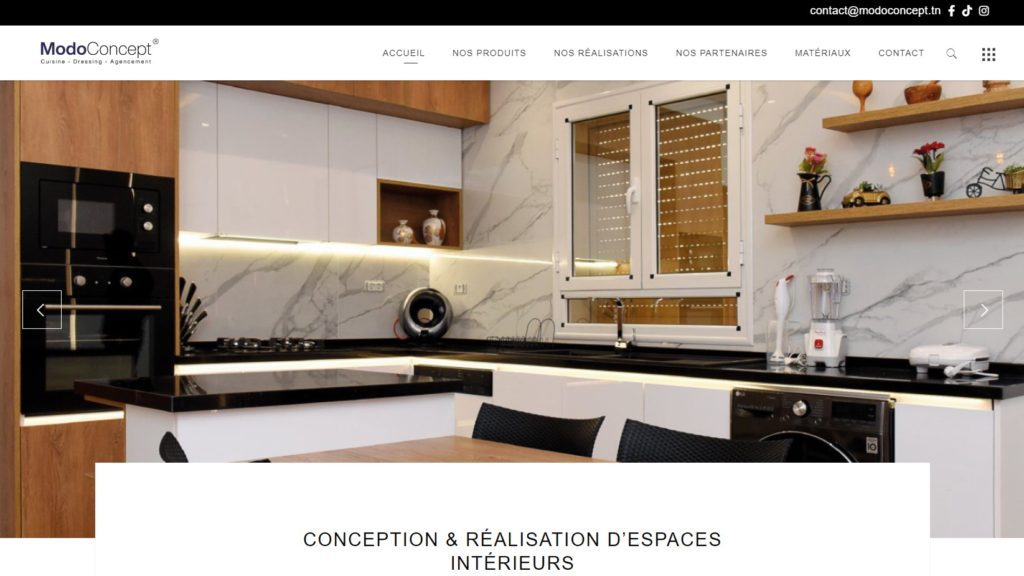
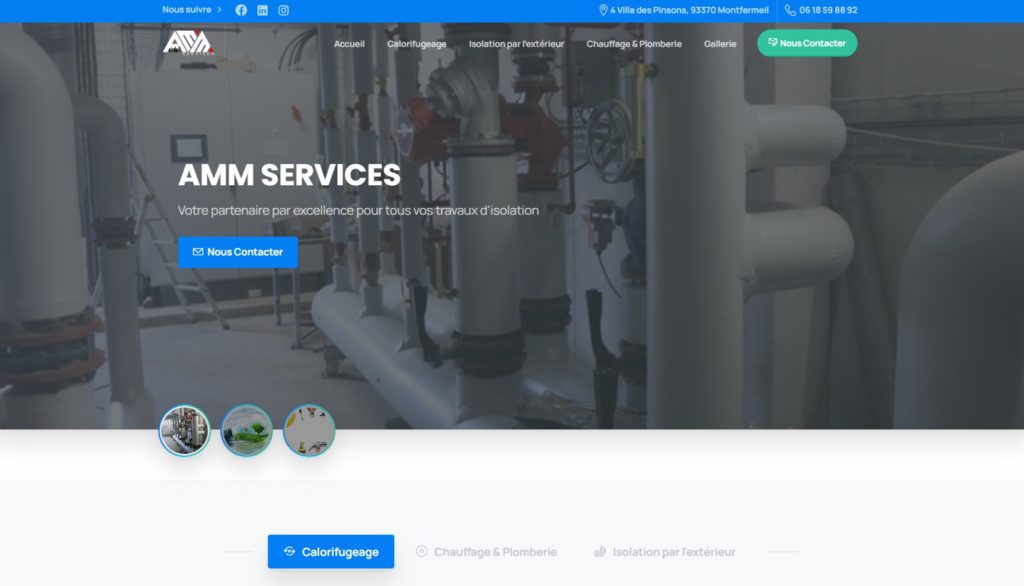
Quelques Références
Liens Utiles
- Sign-in
- Sign-up
- Presse
- Devenir Partenaire
- Politique de Privacy
- Conditions Générales
- Politique des cookies
Contacts
Adresse:
27 Via Alcide De Gasperi, 98066 Patti (ME) Italie
Email:
Téléphone:
+39 379 120 61 28
Newsletter
Gardons toujours contact ! Abonnez-vous à notre newsletter.


Copyright 2023 MBI-NETWORK.COM All Rights Reserved